In the ever-evolving landscape of mental health apps, OCD.app stands out by leveraging artificial intelligence to provide a truly personalized experience for its users. Let’s explore how AI is revolutionizing the way we approach mental health support through this innovative application.
Tailored Tracks: Your Unique Path to healthier thinking
One of the most exciting features of OCD.app is its ability to create dynamic user tracks based on free text input. By analyzing the challenges you describe, the app recommends modules that are most relevant to your specific needs. This personalized approach ensures that you’re not following a one-size-fits-all program, but rather a journey tailored just for you.
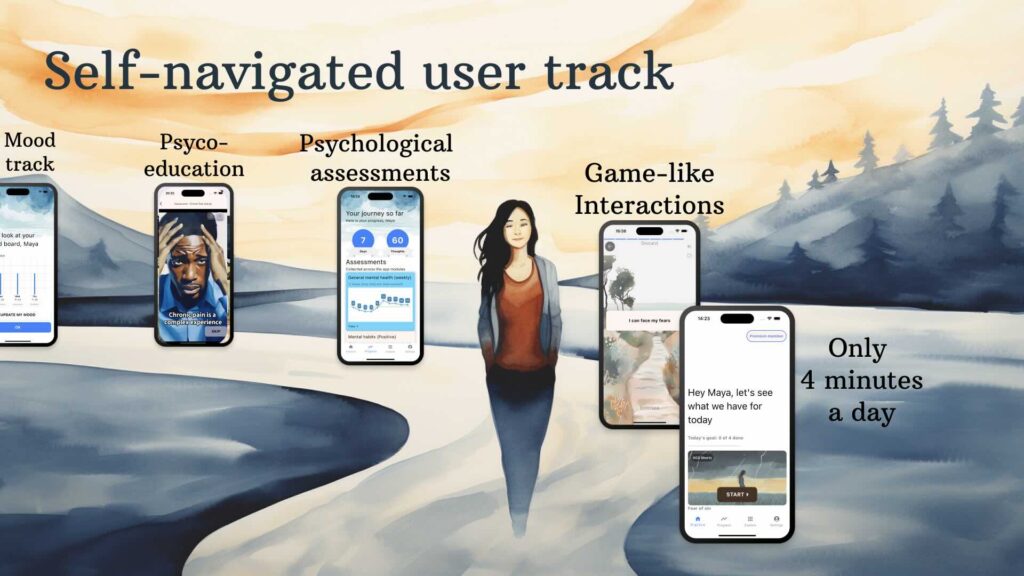
A Wide Range of Support: More Than Just OCD
While OCD is in the name, OCD.app goes far beyond a single focus. With over 20 modules covering a spectrum of mental health concerns, including anxiety, PTSD, mood disorders, grief, relationship conflicts, body image issues, self-esteem, and even chronic pain, the app uses AI to help you navigate the complexities of your mental health landscape.
Understanding Your Thoughts: AI-Powered Cognitive Analysis
One of the app’s most innovative features is its ability to provide dynamic explanations of your thoughts. Using a specially trained AI model, OCD.app can analyze specific thoughts you’re having and explain why they might be helpful or unhelpful. This real-time feedback can be a game-changer in developing healthier thought patterns.
Context-Aware Support: Tips and Psychoeducation
We all need a little extra motivation sometimes, and OCD.app delivers. The app uses AI to generate motivational tips and psychoeducational content based on your current context. Whether you’re having a tough day or celebrating a victory, the app is there to provide the right kind of support at the right time.
Coming Soon: Mood Insights
Looking ahead, OCD.app is developing an exciting new feature: mood insights. By aggregating data from your mood checks, including the specific words you use to describe your feelings, the app will soon be able to provide valuable insights about your emotional trends over time.
The Future of Mental Health Support
By harnessing the power of AI, OCD.app is setting a new standard for personalized mental health support. It’s not just about providing information; it’s about understanding you as an individual and adapting to your unique needs. As we continue to advance in both mental health research and AI technology, we can look forward to even more innovative ways to support our mental well-being.
Remember, while OCD.app is a powerful tool, it’s always important to work with mental health professionals for comprehensive care. Apps like this can be an excellent supplement to traditional therapy, providing support and insights between sessions.
Are you ready to experience a mental health app that truly understands you? Give OCD.app a try and see how AI-powered personalization can make a difference in your mental health journey.











